Leaders Tech Talk: 𝗛𝗼𝗹𝗶 𝗶𝘀𝗻’𝘁 𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗱𝗼𝗺 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗼𝘀. 𝗧𝗵𝗲𝗿𝗲’𝘀 𝗮𝗰𝘁𝘂𝗮𝗹𝗹𝘆 𝗮 𝗽𝗿𝗼𝗰𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗯𝗲𝗵𝗶𝗻𝗱 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗰𝗲𝗹𝗲𝗯𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻.
Why Cyber Resillence is lifeline of Modern Finance : Hear it straight from CISO
Introduction
Cyber resilience has emerged as a strategic imperative for organizations navigating today’s increasingly complex and hostile digital landscape. From a Chief Information Security Officer’s (CISO) viewpoint, cyber resilience transcends traditional cybersecurity defensive measures by emphasizing the organization’s ability to anticipate, withstand, recover from, and adapt to adverse cyber events while ensuring business continuity and sustaining trust among stakeholders
In another words, “Cyber resilience refers to an organization's capacity to prevent, endure, and recover from cybersecurity incidents, ensuring that business operations can continue despite disruptions.”
The Need for Cyber Resilience
As organizations undergo rapid digital transformation, their IT environments become more complex and interconnected. Dependencies on cloud platforms, IoT devices, mobile access, and remote work models expand the potential attack surfaces while increasing exposure to sophisticated cyber threats. The COVID-19 pandemic amplified these trends, underscoring vulnerabilities and the urgency for businesses to build resilience into their digital ecosystems.
On June 2, 2023, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued draft Master Directions focusing on Cyber Resilience and Digital Payment Security Controls for Payment System Operators (PSOs), with the goal of enhancing the protection and safety of digital payment systems run by approved non-bank PSOs. These Directions respond to the rising concerns of cybersecurity risks as India’s digital payment ecosystem expands, emphasizing comprehensive governance and baseline security practices to enhance cyber resilience.
Economic and Social Importance
Cyber resilience is critical not only for protecting organizations but also for securing national infrastructure, safeguarding economic stability, and maintaining public trust. In countries like India, where digital adoption is rapidly growing, resilience mitigates the impact of cybercrime, protects privacy, and ensures the functionality of vital services.
The Growing Stakes in Financial Cybersecurity
Recent data highlight a dramatic surge in cyber attacks targeting the financial sector. According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), annual losses to financial firms from cyber incidents escalated from approximately $300 million in 2017 to $2.2 billion in 2021. These trends underscore the reality that cyber disruptions can pose systemic risks, jeopardizing not just individual institutions but the global financial stability. Based on IBM cost of cyber incident report the average cost of incident is roughly 3-5 million USD.
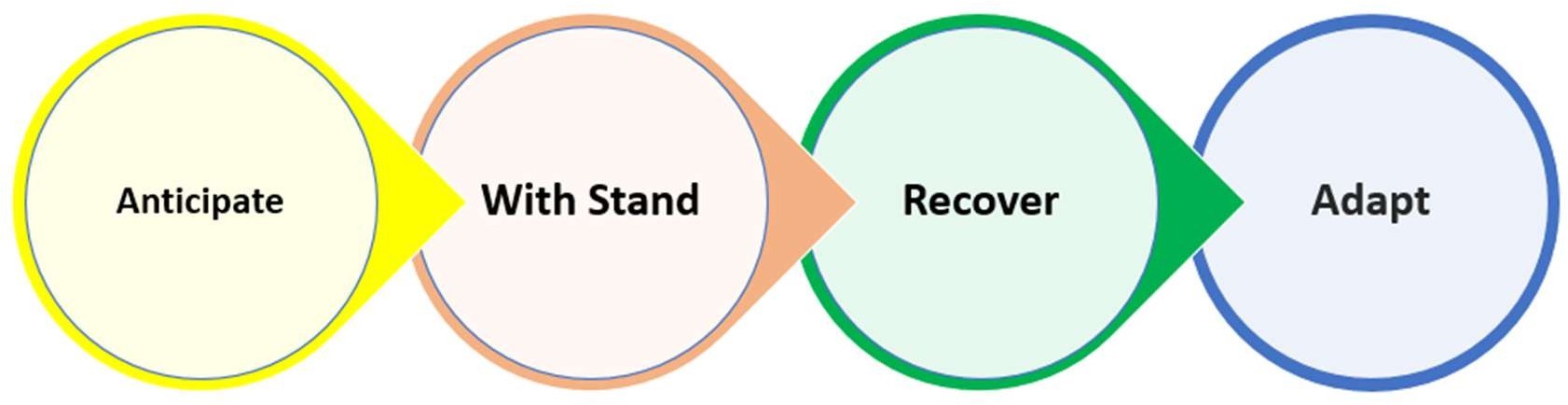
Cyber resilience helps businesses and societies by:
- Anticipating and preparing for cyber incidents.
- Withstanding and absorbing shocks without catastrophic failure.
- Recovering quickly to restore normal operations.
- Adapting continually to evolving threat landscapes.
Key Components of Cyber Resilience
1.Security by Design
Embedding security principles at every stage of system design minimizes risk exposure and enables secure innovation. Approaches such as the principle of least privilege, defense-in-depth, secure defaults, and minimization of attack surfaces ensure that security is integral to systems rather than an afterthought. Organizations are adopting Zero Trust Architecture, which operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify,” requiring thorough verification for every user and device attempting to access the network.
2.Integrated Risk Incident and Crisis Management
Risk management is fundamental, involving the ongoing process of identifying possible threats and evaluating their associated risks. Effective resilience demands ongoing risk assessment, regular system testing, and a well-defined crisis response strategy. Empowering all organizational levels through continuous cybersecurity education promotes early detection and coordinated response to cyber threats.
3.Digital Threat Situational Awareness
Proactively monitoring emerging threats through threat intelligence, penetration testing, and collaborating across the security community enhances early warning capabilities. Understanding attacker behaviors and adapting defenses accordingly fortify the organization's security posture. Advanced threat intelligence solutions enable organizations to detect irregularities and potential threats instantly, allowing for swift action to prevent major damage.
4.Resilient Security Operations
Leveraging automation, machine learning, and analytics strengthens threat detection and incident response. Platforms integrating disparate security tools enable holistic visibility and rapid remediation. Proactive threat hunting uncovers concealed vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them.
Extensive training programs keep employees informed about phishing scams, social engineering tactics, and security best practices, with these awareness initiatives regularly updated to tackle new threats. Since human error remains the leading cause of cybersecurity incidents, employee education is essential for maintaining security.
Why Cyber Resilience is the “Lifeline” of Finance
From the CISO’s viewpoint, cyber resilience transcends mere defense; it is a lifeline that sustains trust, operational continuity, and the financial ecosystem’s integrity. In a sector where milliseconds matter, and monetary transactions depend on seamless IT infrastructure, the ability to withstand and rapidly recover from cyber incidents is non-negotiable.
Protecting Critical Infrastructure: Financial market infrastructures, payment systems, and messaging networks form the backbone of global finance. Cyber resilience ensures these remain uncompromised and operational
- Safeguarding Financial Stability: Uncontained cyber incidents can propagate systemic risks by disrupting interconnected institutions. Effective cyber resilience strategies help contain risks within manageable bounds
- Preserving Customer Confidence: In a sector where reputation is invaluable, effective cyber resilience prevents long-term operational disruptions that jeopardize customer trust and business viability
Challenges and Outlook
- The expanding attack surface with remote work, cloud adoption, and third-party interdependencies require continuous vigilance and adaptive strategies.
- Budget pressures and workforce shortages compel CISOs to prioritize investments in automation, strategic partnerships, and fractional CISO models where full-time leadership is unavailable.
- Increasing regulatory requirements sharpen the focus on documented resilience capabilities, mandating measurable improvements and transparent external reporting
Current CISO priorities emphasize practical implementation. Organizations are enhancing their incident response and business continuity plans by merging cyber resilience with operational risk and third-party management. This effort involves establishing strong backup procedures and utilizing flexible security tools and data management solutions. As cyber threats progress rapidly, the organizations most prepared will be those able to remain operational during disruptions and quickly restore normal activity after an incident occurs.
For CISOs confronting these challenges, achievement lies less in blocking every threat and more in developing businesses that can endure, adapt to, and ultimately strengthen through unavoidable cyber risks. The direction is evident: cyber resilience is no longer merely a security tactic, but is now central to the survival of organizations facing a continually more aggressive digital landscape.
Conclusion
For today’s CISOs, cyber resilience is not simply a technical issue but a comprehensive organizational imperative encompassing people, processes, technology, and governance. It demands a shift from prevention-only mindsets to pragmatic preparedness, rapid recovery, and continuous adaptation—all aligned tightly with business objectives. CISOs who successfully operationalize resilience frameworks position their organizations to thrive despite inevitable cyber challenges, safeguarding long-term value and stakeholder trust.